Esophageal Sphincter Histology Biology Diagrams
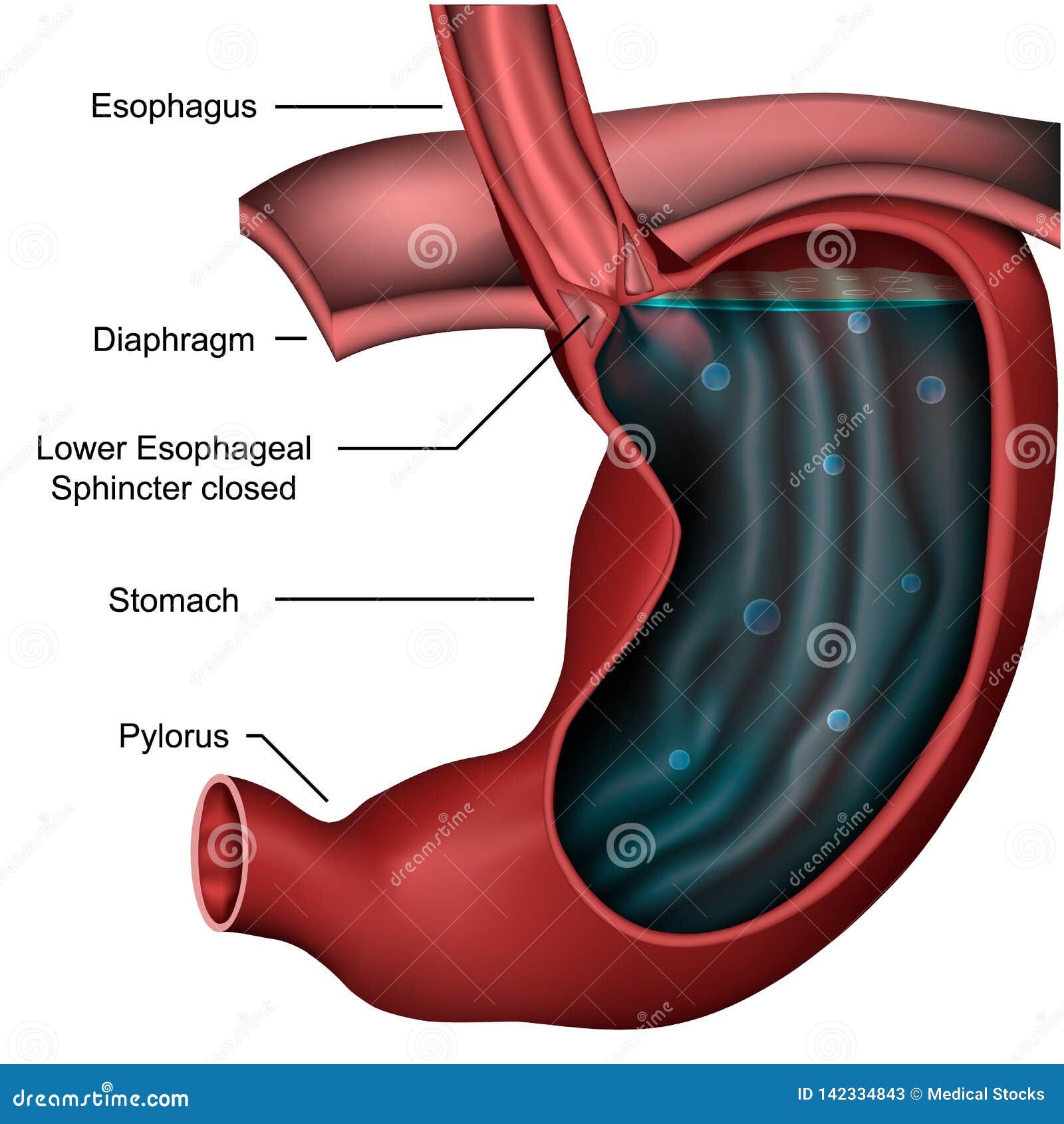
Esophageal Sphincter Histology Biology Diagrams Lower esophageal sphincter Distal 2-4 cm esophageal high pressure zone defined by manometry. Corresponds to vestibule on esophagram. Prevents gastroesophageal reflux. Drugs and many types of food and drink affect lower esophageal sphincter and can lead to reflux. Glucagon relaxes the lower esophageal sphincter when used for air-contrast upper gastrointestinal examination. The tubular esophagus Abstract: The upper esophageal sphincter (UES), also known as the pharyngoesophageal segment (PES), is a 4-cm segment of the digestive tract that separates the esophagus from the pharynx and larynx. This narrative review represents an overview of the anatomy and physiology of this critical component of the airway protective mechanism. There are two sphincters present in the oesophagus, known as the upper and lower oesophageal sphincters. They act to prevent the entry of air and the reflux of gastric contents respectively. Upper Oesophageal Sphincter The upper sphincter is an anatomical, striated muscle sphincter at the junction between the pharynx and oesophagus.
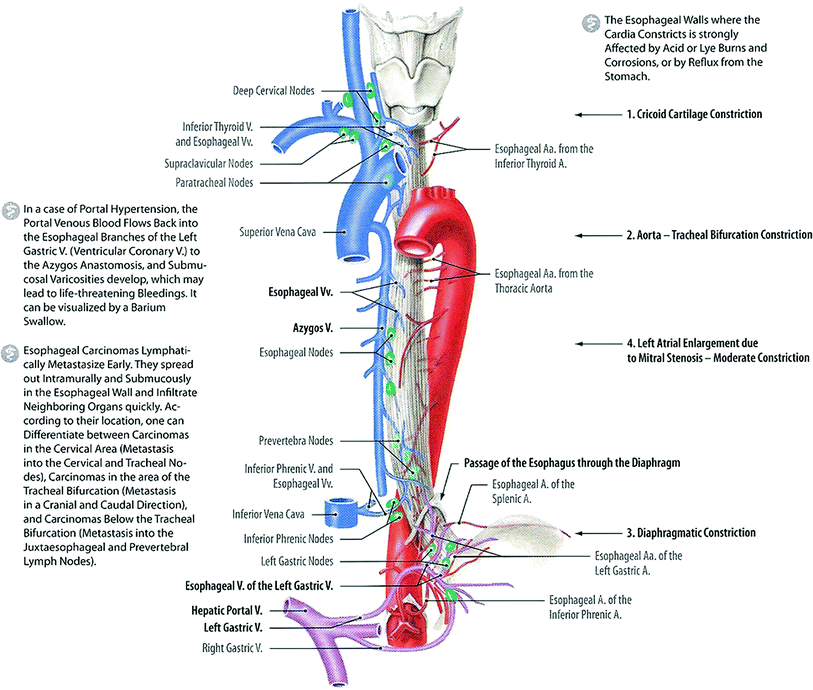
Upper esophageal sphincter is composed of all skeletal muscles and lower esophageal sphincter of all smooth muscles. Based on the studies in mice embryo, esophagus is comprised of entirely smooth muscles at the beginning that slowly transdifferentiate into the skeletal muscles during later embryological age until few days after birth [54]. The upper esophageal sphincter (UES) is a high-pressure zone at the transition of the pharynx and the cervical esophagus. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is a high-pressure zone located where the esophagus meets the stomach and protects the esophagus from the reflux of gastric contents. The lower esophageal sphincter is a valve between your esophagus and stomach. It prevents stomach contents from going back up the esophagus.
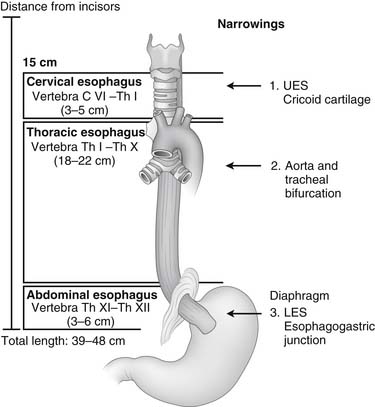
Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation Biology Diagrams
This article describes the anatomy of the esophagus. Click here to learn more about its sphincters, arteries, veins, and nerves at Kenhub! Esophagus: Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy Layers Mucosa (Squamous Epithelium) Submucosa Muscularis Propria (Longitudinal) Upper 1/3: Striated Lower 2/3: Smooth No Serosa Importance: CA Spreads Through Lymphatics Sphincters Upper Esophageal Sphincter (UES) Cricopharyngeus Muscle 15 cm From Incisors Most Common Site of Iatrogenic Perforation and Foreign Body Prevents Air Swallowing Innervation