Editorial Induced cell senescence as a therapeutic Biology Diagrams
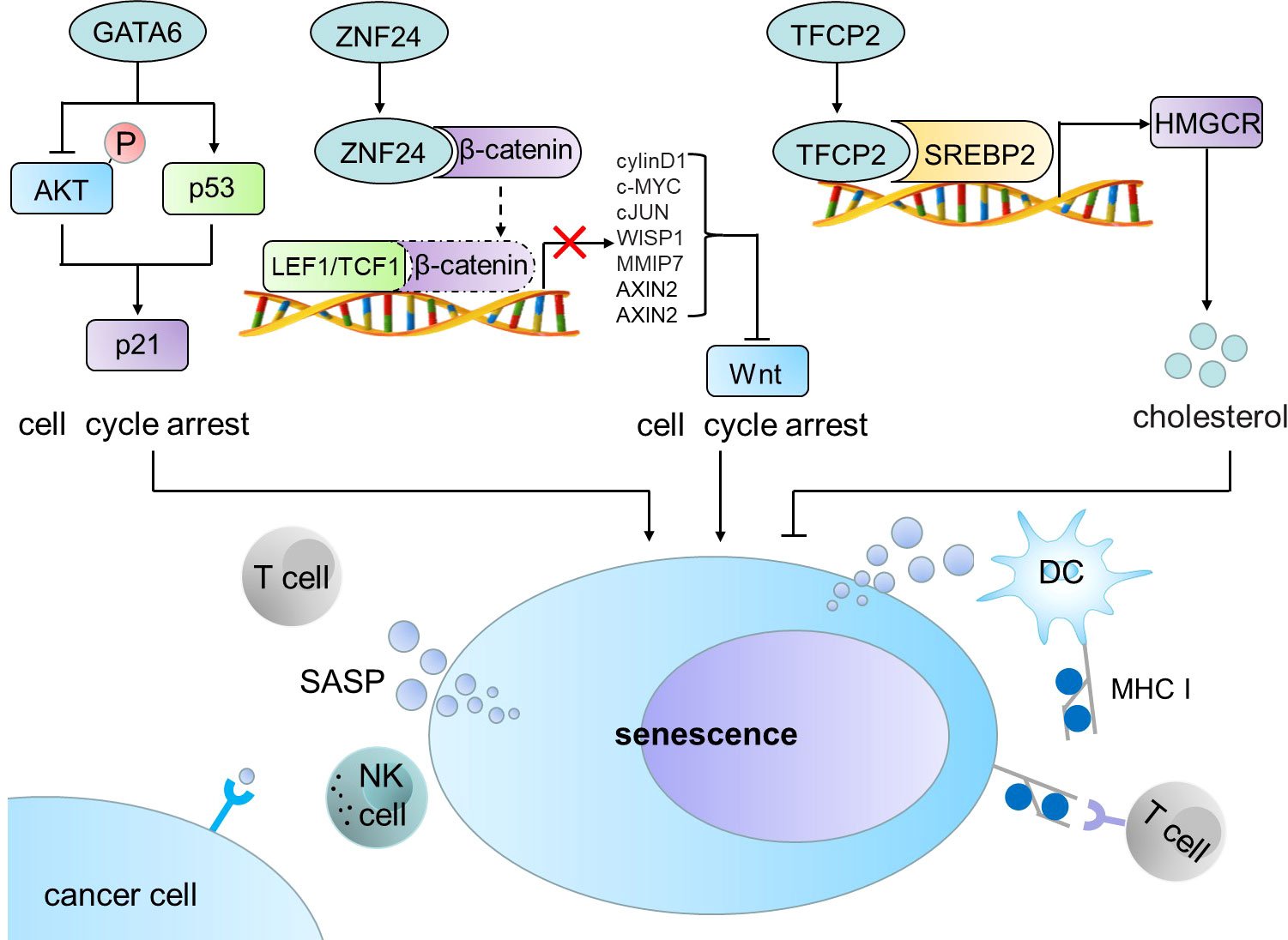
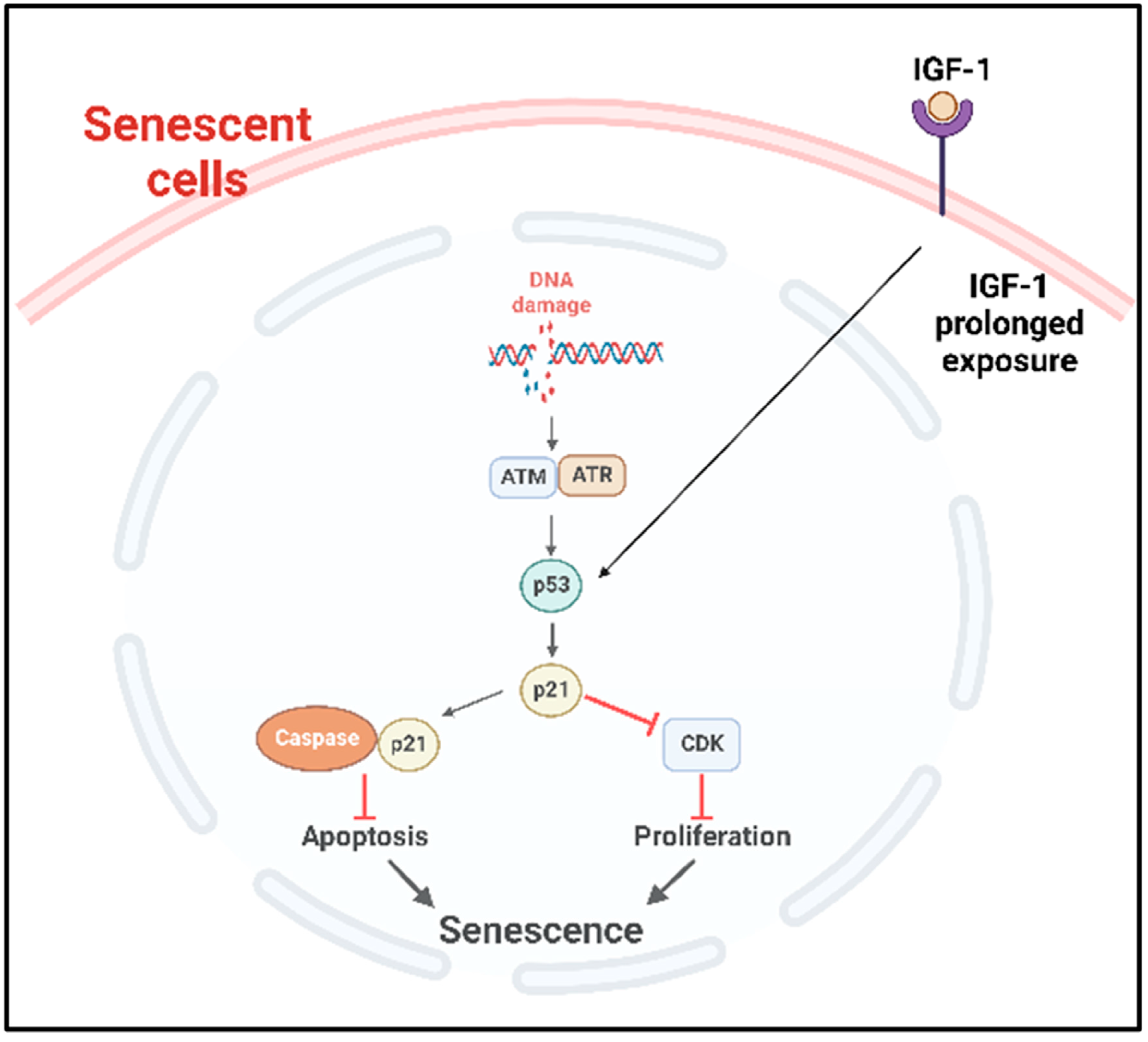
Editorial Induced cell senescence as a therapeutic Biology Diagrams The senescence-associated irreversible cell-cycle arrest is mainly characterised by the activation of two cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, p21 WAF1/Cip1 (p21) and p16 INK4a (p16), which halt cell-cycle progression in G0/G1 phase. Although extensively used as a senescence biomarker, activation of a state of irreversible growth arrest is
These changes have been linked to both the cell-autonomous and paracrine aspects (that is, the effect on surrounding cells) of senescence-associated proliferation arrest. Senescence-associated
associated ribosome biogenesis defects contributes to cell ... Biology Diagrams
Loss of SIRT1 activity is associated with multiple aspects of senescence, including SASP activation 91 and cell cycle arrest 92, as well as several senescence-associated degenerative pathologies Cellular senescence is a stable cell cycle arrest that can be triggered in normal cells in response to various intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli, as well as developmental signals. Mechanisms of Cellular Senescence: Cell Cycle Arrest and Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 29:9:645593. doi: 10.3389/fcell

Cellular senescence is a highly stable cell cycle arrest that is elicited in response to different stresses. By imposing a growth arrest, senescence limits the replication of old or damaged cells. A variety of stressors induce senescence-associated growth arrest. Cell cycle exit is regulated by induction of the p16 INK4a /Rb and p53/p21

The metabolic roots of senescence: mechanisms and ... Biology Diagrams
(D-G) Transcriptional expression of cell cycle arrest markers (p16 INK4a, p21 WAF1) and SASP factors (IL-6, IL-1b) within the hippocampus of vehicle-treated cognitively stratified and senolytic-treated aged male mice. (H, I) Quantification and representative images of senescence-associated beta-galactosidase staining within the hippocampus.
